How to identify and control poison hemlock
Poison hemlock (Conium maculatum) was originally brought to the United States in the 1800s as an ornamental garden plant (another good idea gone awry) and is now found throughout North America.In Michigan, it has been reported in several counties throughout the Lower Peninsula and in a few in the Upper Peninsula, according to Michigan Flora Online. Recently, we have identified it in several locations, including, Kalamazoo, St. Joseph, Van Buren and Ottawa counties.
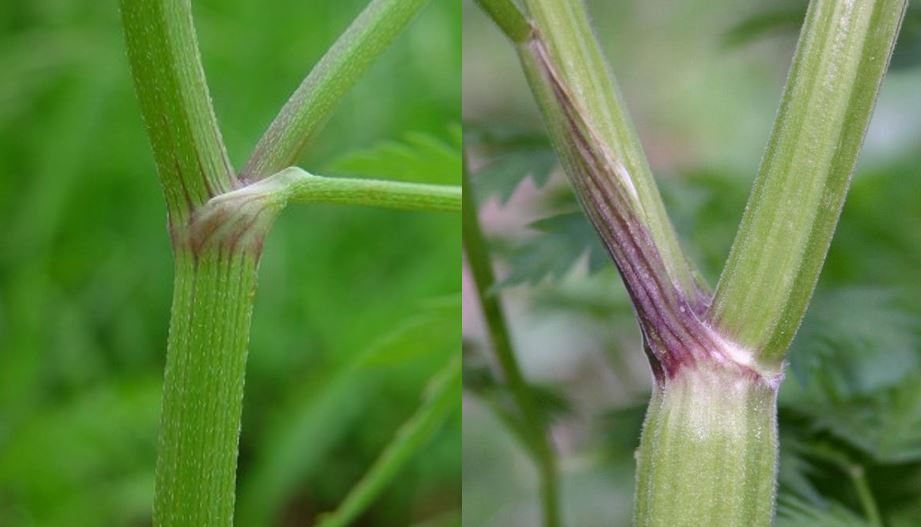
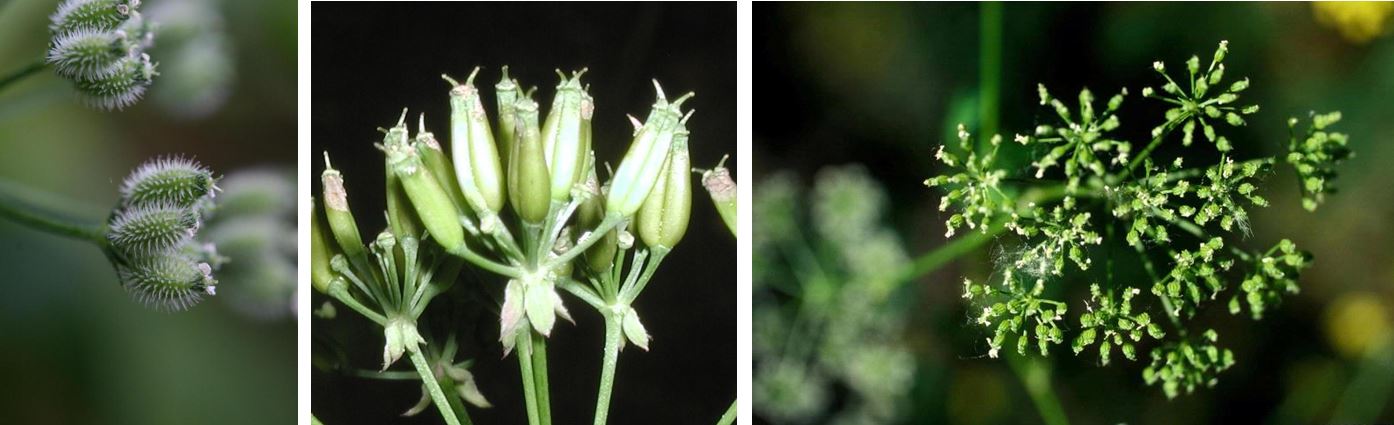
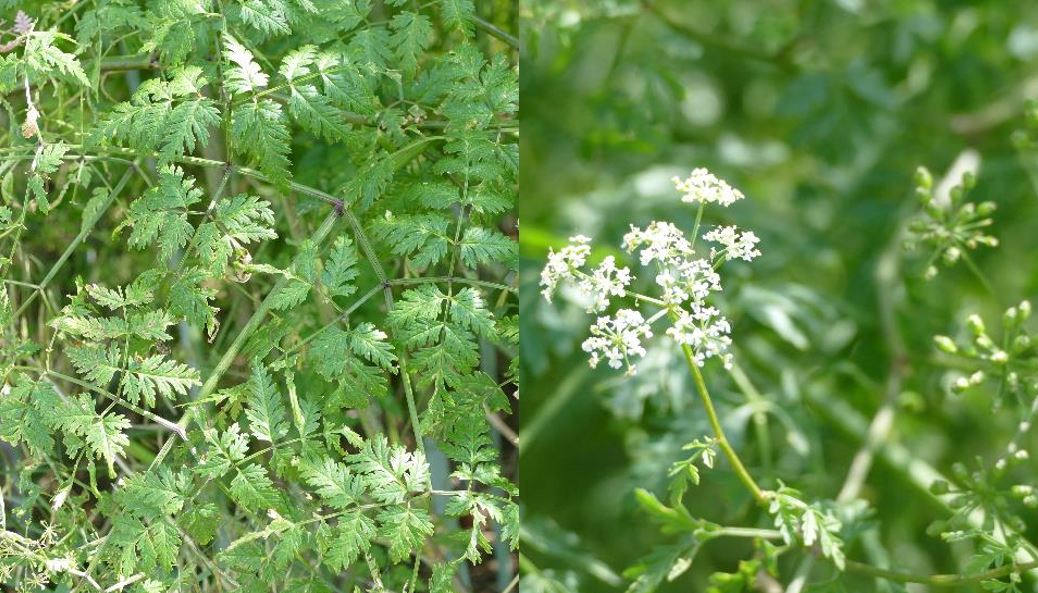
Poison hemlock is a biennial that forms a rosette its first year, often going unnoticed, and then produces white umbel flowers (umbrella-like) on tall stems in the spring-summer of its second year. These types of flowers are common in the carrot family and are similar to wild carrot (also known as Queen Anne’s lace, Daucus carota), which is often mistaken for this plant at younger stages. The second-year stems of poison hemlock are hairless and have purple spots, which help distinguish it from wild carrot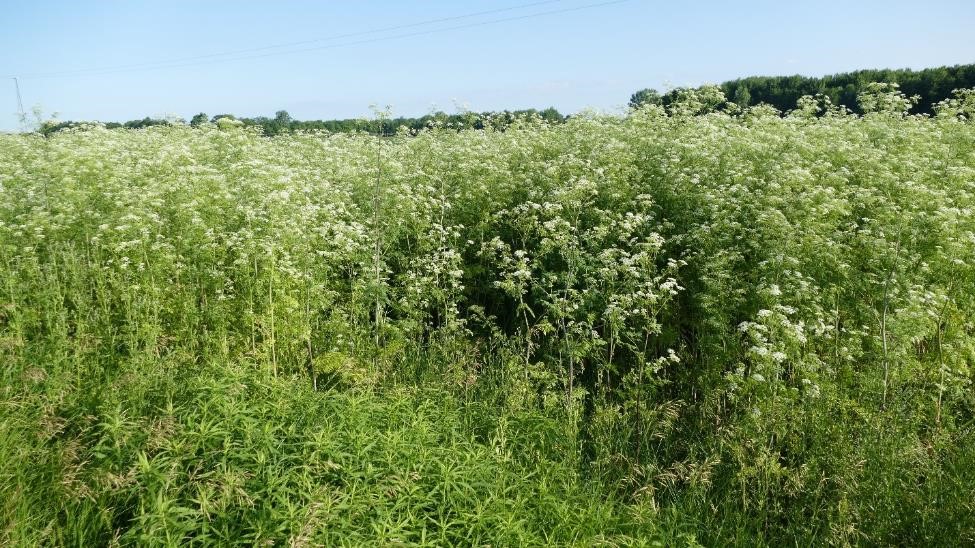
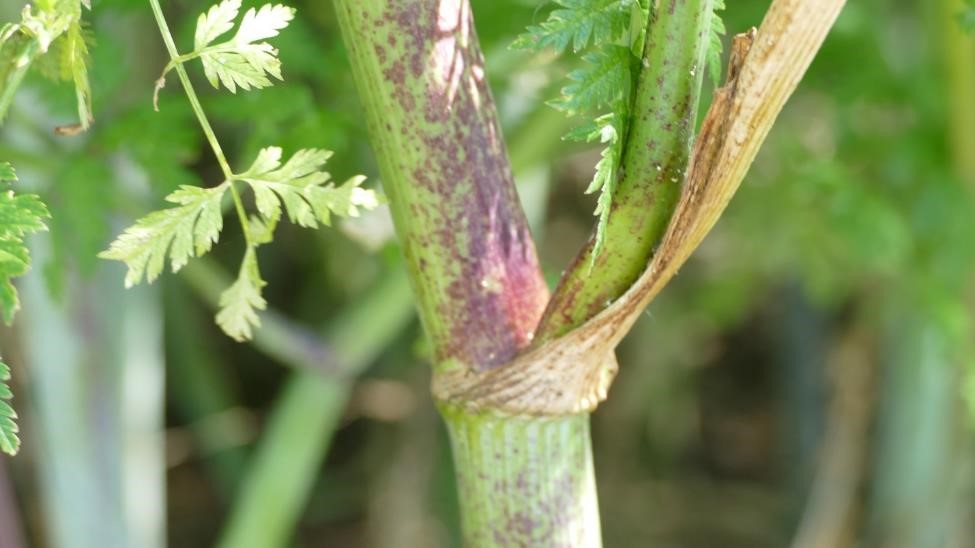

Other look-alikes that can grow in disturbed areas, woodland edges and along road sides include Japanese hedge parsley (Torilis japonica) and false chervil (Anthriscus sylvestris). Japanese hedge parsley has lacey, finely divided leaves like poison hemlock, but has fine hairs along the leaves and stem and does not have the distinct purple spotting. There are also hooked hairs on the fruit. False chervil fruit are narrowly egg-shaped. Stems are hairy, ribbed and the leaf sheath wraps around the stem. Both Japanese hedge parsley and false chervil generally do not reach more than 6 feet at maturity.
Poison hemlock reproduces exclusively by seed. According to Mitich LW, 1998, it can produce up to 38,000 seeds per plant that generally fall near the mother plant but can be dispersed by water, birds and other wildlife. Seeds can germinate immediately or lay dormant for up to six years. The plant will die soon after it sheds seed, but the stems will remain standing and slowly release seed into winter. More detailed information about poison hemlock can be found at USDA's Poison Hemlock website and University of California's Poison Hemlock website.
All parts of poison hemlock are toxic if ingested by humans and it is infamously known as the form of death chosen by Socrates. It is also highly toxic to livestock and wildlife. More information can be found about its toxicity at Poison Control.
The phototoxic compound (i.e., furanocoumarins) that causes blisters in those who touch giant hogweed is also present in the sap of all other plants in the carrot family, including poison hemlock. Contact with the sap can cause sensitivity to UV light from the sun, resulting in blisters. The difference is that people are much less likely to encounter the sap on carrot family species other than giant hogweed as it is inside the stem, whereas on giant hogweed it is also present on the exterior.
If you find any poison hemlock in your yard or pasture, you can dig up plants, including the tap roots, for removal. Given the reproductive capacity of this plant, remove it as soon as possible to avoid perpetuating the infestation. Wear gloves, long sleeves, pants, socks and shoes to protect your skin from the sap. Compost or dispose plants with yard waste. Poison hemlock is not considered an invasive species in Michigan, therefore it should not be disposed with regular trash. Do not burn plants to prevent any accidental inhalation. Mowing or weed whacking will not kill the plant but can reduce seed production in second year plants. If you are mowing or weed whacking in areas infested with poison hemlock, wear protective eyewear and a dust mask to prevent exposing your eyes and lungs to small particles.
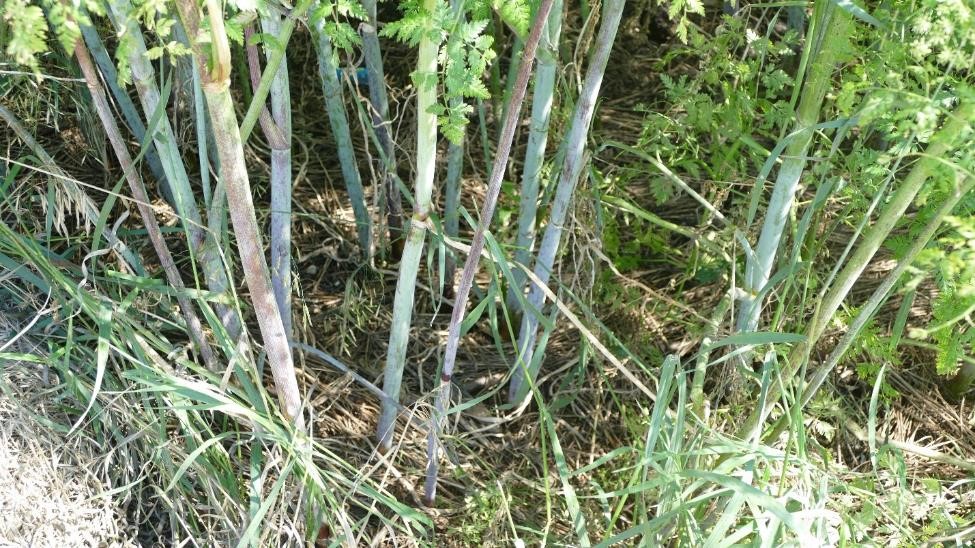

Herbicides can also be effective for controlling poison hemlock when sprayed on first year plants and small plants before flowering in the second year. Mature, flowering plants like the ones in the photos will not likely be chemically controlled, and mechanical control measures should be used prior to seed set.
Choosing a herbicide will depend on the desirable surrounding vegetation. If poison hemlock is growing amongst grasses, synthetic auxin herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, clopyralid and triclopyr will selectively control the poison hemlock, leaving the grass unaffected. If the poison hemlock is in a bare ground area or other area where the surrounding vegetation is not of importance, a broad-spectrum herbicide such as glyphosate (active ingredient in Roundup Weed and Grass Killer, among others) can be effective.
Note that glyphosate will injure or kill other plants contacted during application, so care is needed to avoid green plant material, exposed roots and injured bark of desired plants. If the poison hemlock is growing among desirable broadleaf plants or shrubbery, mechanical removal is advised.